Description
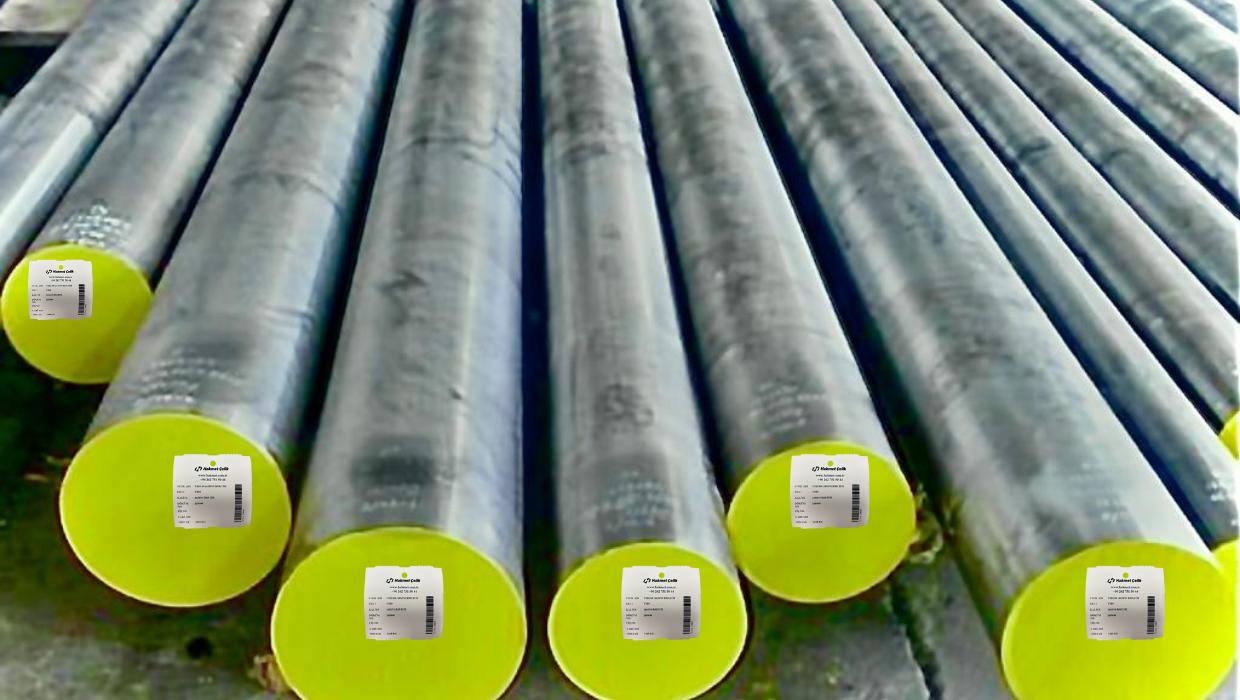
Structural Steels
Demand for iron and steel directly depends on the overall state of the country’s economies, infrastructure investments, housing investments and the level of development of the construction sector in general. In this context, structural steels, which have the most significant share among the steels produced all over the world, hold the most important place. Structural steels, which are advantageous in terms of price and availability compared to other steels, constitute 75-80% of the steels used in the market.
Steels used in industrial and structural applications are called “”Structural Steels””, which contain manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), copper (Cu) and sulfur (S) elements originating from the production raw materials and production method, especially considering the tensile strengths and yield limits, which are hot-formed, normalized and sometimes cold-drawn, and do not contain alloy elements with low carbon content, especially phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N).
Structural steels can be divided into different subgroups as hot-formed (thermomechanically treated), cold-drawn, normalized, fine-grained, weldable, corrosion resistance improved, quenched and primed high yield strength steels.
Structural steels have a wide range of uses in the manufacturing and building industry as low-carbon, unalloyed rolling and normalization rolling plates. They are produced and put into use with yield/tensile strengths and low-temperature toughness properties varying with the control and orientation of microalloying and/or grain size. The most important manufacturing methods applied to these skewers are cutting, machining, cold and hot deformation and welding. Perhaps the most important of these methods is welding, with low carbon contents, the weldability of these steels is defined as good. The strength values specified in this group of steels are the main feature to be fulfilled.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.